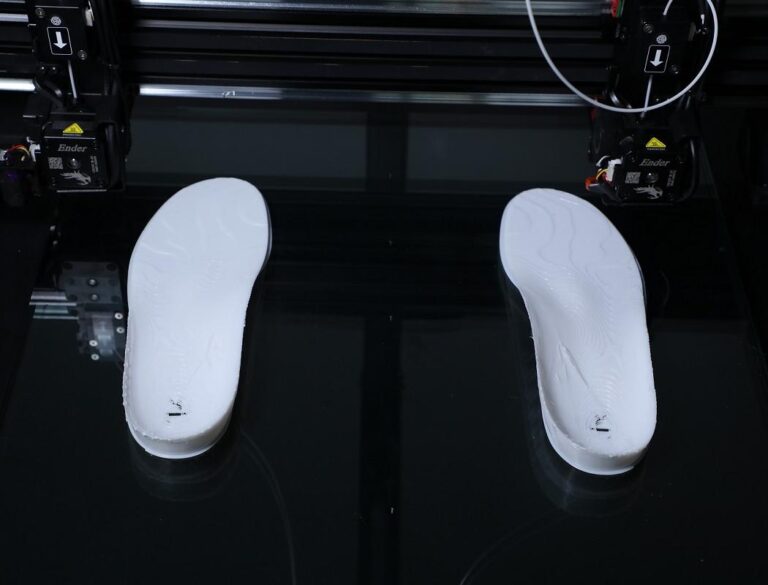
In today’s fast-paced world, bringing ideas to life quickly and efficiently is crucial. Rapid prototyping with 3D printing has revolutionized the way products are designed and developed, providing an agile and cost-effective solution for industries ranging from automotive to consumer goods. This technology empowers designers and engineers to transform digital concepts into physical models in a matter of hours, accelerating the innovation process and reducing the time to market.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the basics of rapid prototyping, how 3D printing is used in the process, examples of rapid prototypes, types of prototyping, and the key advantages that make this technology indispensable.

What is Rapid Prototyping with 3D Printing?
Rapid prototyping refers to the process of quickly creating a physical model or prototype of a design idea to test its form, fit, function, and usability. Traditionally, prototyping involved complex machining or molding techniques that were time-consuming and costly.
With the advent of 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, rapid prototyping has become more accessible and versatile. 3D printing builds objects layer by layer from a digital model, allowing for highly accurate and detailed prototypes to be created in a fraction of the time required by traditional methods.
The key features of rapid prototyping with 3D printing include:
- Speed: Prototypes can be printed within hours.
- Customization: Designs can be adjusted and reprinted easily.
- Cost-Effectiveness: No need for expensive tooling or molds.
How is 3D Printing Used in Prototyping?
3D printing plays a pivotal role in rapid prototyping by enabling designers and engineers to:
- Visualize Designs: Transform CAD (computer-aided design) models into tangible objects to evaluate the look and feel of a product.
- Test Functionality: Assess mechanical properties, ergonomics, and usability by creating functional prototypes.
- Iterate Quickly: Make adjustments to the design, print revised versions, and refine the prototype until the desired outcome is achieved.
- Communicate Ideas: Provide stakeholders and clients with physical models for feedback, improving collaboration and decision-making.

Common Industries Using 3D Printing for Prototyping
- Automotive: Engineers can create prototypes of car parts to test performance and durability.
- Healthcare: Medical devices and prosthetics can be quickly prototyped for testing and fitting.
- Consumer Goods: From electronics to household items, companies can create prototypes to evaluate functionality and aesthetics.
- Aerospace: Complex components can be prototyped to test design feasibility and material properties.
What is an Example of a Rapid Prototype?
One practical example of a rapid prototype is the creation of a custom ergonomic mouse for computer users.
Process:
- Designers use CAD software to create a digital model of the mouse, ensuring it fits the shape of an average user’s hand.
- A 3D printer produces the mouse prototype using durable materials like ABS or PETG.
- Users test the prototype for comfort, button placement, and overall usability.
- Based on feedback, the design is refined, and a new prototype is printed.
This iterative process allows manufacturers to perfect their products before committing to large-scale production, minimizing costly errors and ensuring customer satisfaction.
What are the Three Types of Rapid Prototyping?
There are three primary types of rapid prototyping, each serving different purposes depending on the stage of development:
1. Visual Prototyping
These prototypes are used to assess the aesthetics and dimensions of a product. While they may not be functional, they help visualize the final product’s appearance. For instance, a designer might create a visual prototype of a smartphone casing to evaluate its shape and color options.
2. Functional Prototyping
Functional prototypes are designed to mimic the mechanical properties of the final product. These are essential for testing usability, durability, and performance. For example, engineers might prototype a drone’s propeller to ensure it can withstand operational stresses.
3. Concept Prototyping
These early-stage prototypes focus on demonstrating the basic idea or concept behind a product. Concept prototypes are often used to pitch ideas to stakeholders or test general feasibility. For instance, a simple 3D-printed model of a foldable chair could demonstrate the concept without incorporating all mechanical features.
What are the Advantages of Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping with 3D printing offers numerous benefits that make it a game-changer in product development:
1. Speed and Efficiency
Prototypes can be created within hours, enabling faster iteration cycles. This reduces the overall time required to bring a product to market, giving companies a competitive edge.
2. Cost Savings
Traditional methods like CNC machining or injection molding require expensive tooling, which is not economical for low-volume production. 3D printing eliminates the need for molds, significantly lowering costs.
3. Design Flexibility
3D printing allows for complex geometries and intricate designs that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. This opens up new possibilities for innovation.
4. Early Problem Detection
Prototypes enable designers to identify and resolve design flaws early in the development process, reducing the risk of costly errors during production.
5. Improved Collaboration
Physical prototypes enhance communication among teams, stakeholders, and clients, making it easier to gather feedback and align on the final design.
6. Sustainability
3D printing uses only the material needed for the part, reducing waste compared to subtractive manufacturing methods. Additionally, some 3D printers can use recycled materials, further enhancing sustainability.
The Future of Rapid Prototyping
As 3D printing technology continues to evolve, the future of rapid prototyping looks promising:
- Advances in Materials: From bio-compatible materials to high-strength composites, new materials will expand the applications of 3D prototyping.
- Integration with AI: AI-powered software will optimize designs for 3D printing, enhancing efficiency and reducing material usage.
- Wider Accessibility: Desktop 3D printers are becoming more affordable, enabling startups and small businesses to access professional-grade prototyping capabilities.
- Sustainable Practices: Recycling initiatives and renewable materials will further reduce the environmental impact of rapid prototyping.
Conclusion
Rapid prototyping with 3D printing has become an indispensable tool for innovators, enabling them to visualize, test, and refine ideas with unprecedented speed and precision. Whether you’re a designer creating the next big consumer gadget or an engineer solving complex mechanical challenges, 3D printing empowers you to bring your concepts to life efficiently and effectively.
By leveraging the advantages of rapid prototyping, businesses can stay ahead of the competition, minimize risks, and deliver products that resonate with customers. The future of innovation is here, and it’s being built layer by layer with 3D printing.