Table of Contents
3D printing has dramatically transformed manufacturing, offering faster production, customization, and reduced costs. One specific area where it shines is in creating 3D printed jigs and fixtures. These essential tools play a crucial role in enhancing manufacturing accuracy, speeding up production times, and improving overall efficiency. In this blog, we’ll dive into what jigs and fixtures are in the context of 3D printing, their benefits, the best materials used for printing, and why these tools are invaluable in modern manufacturing.

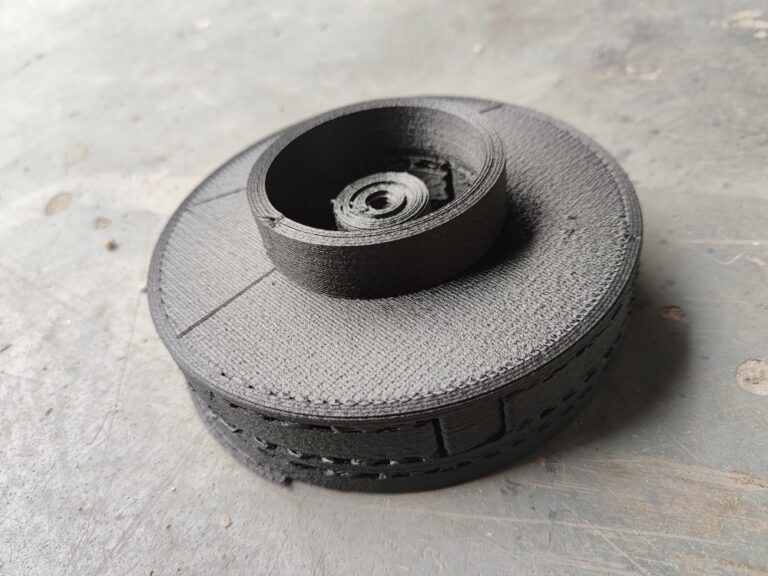
What Are 3D Printed Jigs and Fixtures?
In the world of manufacturing, jigs and fixtures are custom tools used to simplify and speed up assembly, improve accuracy, and secure parts in place during the production process. Traditionally, these tools are machined from metals or other rigid materials, but 3D printing has opened up new possibilities for producing them faster and more cost-effectively.
With 3D printing, manufacturers can create jigs and fixtures in-house, allowing for rapid customization and fine-tuning of designs. These tools can be printed using strong and durable materials like carbon fiber-infused plastics, which make them robust enough for demanding industrial use. From automotive manufacturing to aerospace engineering, 3D printed jigs and fixtures are becoming an integral part of modern production lines.
What is a Jig in 3D Printing?
A jig in 3D printing is a tool designed to guide the positioning or movement of parts or components during assembly, disassembly, or bonding processes. By ensuring parts are aligned correctly, jigs help improve accuracy and minimize human error.
There are several types of jigs used in 3D printing:
1. Assembly Jigs
Assembly jigs help position components for fastening or welding during the assembly process. They ensure that parts fit together correctly and are held in place securely, improving accuracy during production. In the automotive industry, for instance, assembly jigs can be used to align car body panels perfectly.
2. Disassembly Jigs
Disassembly jigs are used to aid in the dismantling of components. These jigs make it easier to remove parts without causing damage, especially when precision is required. In maintenance and repair operations, disassembly jigs are essential for taking apart complex assemblies with minimal risk.
3. Bonding Jigs
Bonding jigs ensure that two parts are held securely together while adhesives or other bonding agents cure. In industries where strong joints are required, bonding jigs are used to apply consistent pressure, ensuring uniform adhesion and proper alignment.
What is a Fixture in 3D Printing?
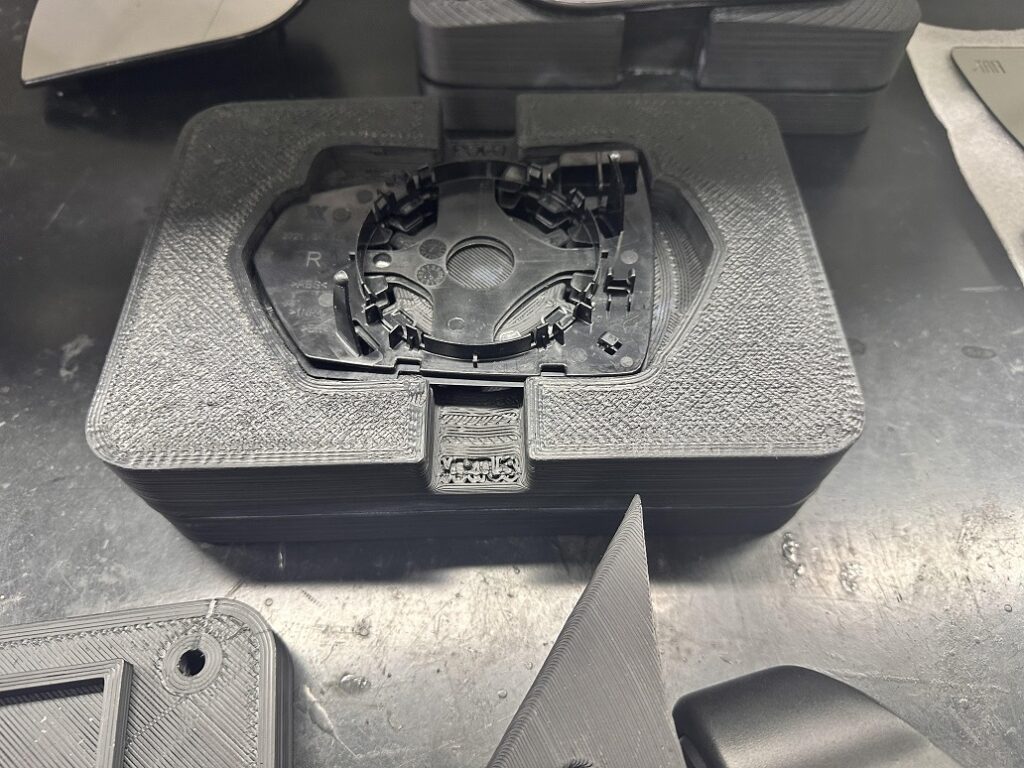
A fixture is a tool that securely holds a component in place during operations like machining, inspection, or assembly. Fixtures are critical for maintaining stability and ensuring precision, especially when parts need to be held still for extended periods.
1. Assembly Fixtures
Assembly fixtures hold parts in place while they are being worked on. These fixtures are custom-designed to fit specific parts, ensuring that they are held securely during processes like welding, drilling, or riveting. By using 3D printed assembly fixtures, manufacturers can ensure that each component is positioned accurately for assembly.
Inspection Fixtures
Inspection fixtures hold parts securely during quality control inspections. They help inspectors measure the dimensions, geometry, and surface quality of parts with greater accuracy. 3D printed inspection fixtures can be customized for specific components, improving the precision and reliability of inspection processes.
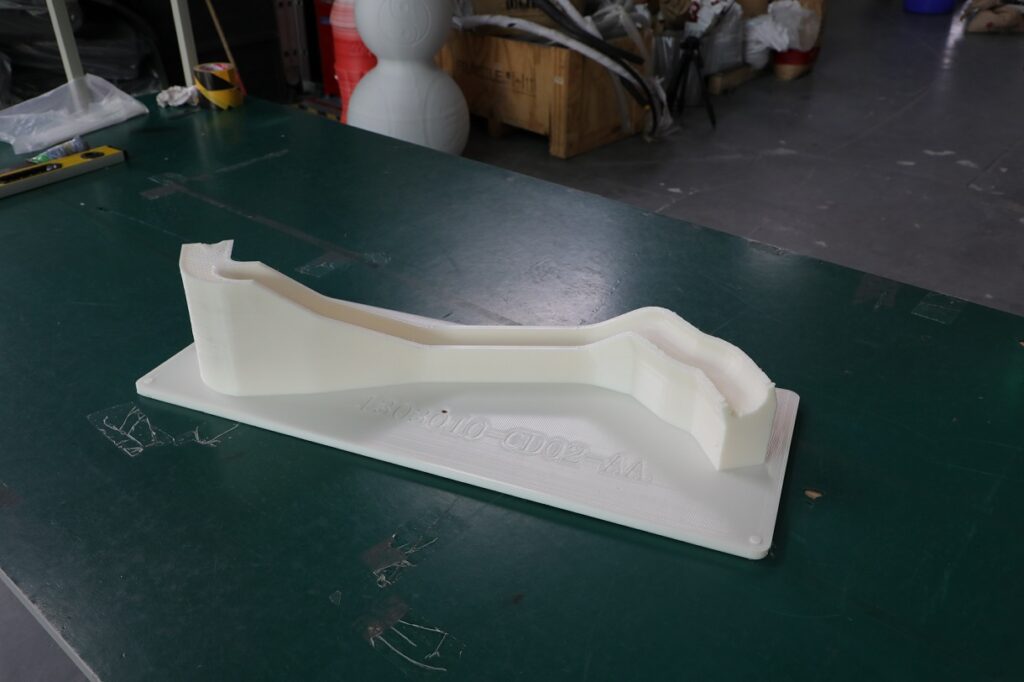

What's the Difference Between a Jig and a Fixture?
While the terms “jig” and “fixture” are often used interchangeably, they serve different purposes in manufacturing:
Jigs
A jig is a tool that guides the movement or placement of another tool, such as a drill or saw, ensuring accurate positioning during operations. Jigs are not fixed in place and are designed to move with the tool or part being worked on.
Fixtures
A fixture, on the other hand, is a tool that holds a part or component firmly in place, preventing movement during machining, assembly, or inspection. Unlike jigs, fixtures are stationary and are designed to keep parts secure during the process.
Benefits of Utilizing Jigs and Fixtures
The use of 3D printed jigs and fixtures offers several distinct advantages over traditional manufacturing methods:
1. Increased Accuracy
3D printed jigs and fixtures are designed to meet precise specifications, reducing the chances of errors during the manufacturing process. By ensuring that parts are properly aligned and held in place, these tools improve the overall quality of the final product.
2. Faster Delivery
Traditional methods for producing jigs and fixtures involve complex machining processes that can take days or weeks. 3D printing drastically reduces lead times, allowing manufacturers to produce custom jigs and fixtures within hours, enhancing production efficiency.
3. Reduced Cost
3D printing jigs and fixtures are more cost-effective than traditional manufacturing, especially for low-volume or custom designs. Materials like carbon fiber-reinforced plastics are cheaper than metals, and in-house production eliminates the need for outsourcing.
4. Customization and Improved Performance
3D printing allows for complete customization of jigs and fixtures, tailoring them to specific tasks or parts. The flexibility of additive manufacturing means that intricate geometries and lightweight designs can be easily achieved, improving the performance of the tool.
Best Plastic Materials for 3D Printed Jigs and Fixtures
Choosing the right material for 3D printed jigs and fixtures is crucial for ensuring durability, strength, and reliability. Here are some of the top materials used in industrial 3D printing for these tools:

1. PA+CF (Polyamide with Carbon Fiber)
PA+CF is a carbon fiber-reinforced polyamide (nylon) material that offers excellent strength, rigidity, and thermal resistance. This material is known for its ease of printing, resistance to warping, and high Z-axis strength, making it ideal for industrial applications. PA+CF can withstand temperatures up to 150°C, making it suitable for use in demanding environments like aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
2. ABS+CF (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene with Carbon Fiber)
ABS+CF is a carbon fiber-infused version of traditional ABS plastic. It combines the ease of use of ABS with the added strength and rigidity of carbon fiber. ABS+CF is lightweight, durable, and resistant to impact, making it a popular choice for jigs and fixtures in assembly lines or for parts that endure heavy usage.
3. PC+CF (Polycarbonate with Carbon Fiber)
PC+CF is a high-performance material that blends the impact resistance and strength of polycarbonate with the rigidity of carbon fiber. This material is ideal for jigs and fixtures that need to withstand high mechanical stress or harsh environments. PC+CF is particularly useful in the automotive and aerospace industries, where durability is critical.
Final Thoughts
3D printing has revolutionized the way manufacturers create jigs and fixtures, providing enhanced accuracy, faster delivery, and reduced costs. With the ability to customize tools for specific applications and use advanced materials like carbon fiber-reinforced plastics, 3D printed jigs and fixtures are now an integral part of modern manufacturing processes.
As industries continue to embrace additive manufacturing, the use of 3D printed jigs and fixtures will only grow, offering even greater flexibility and innovation in production lines. Whether you’re looking to improve assembly efficiency or enhance inspection accuracy, 3D printed jigs and fixtures provide a cost-effective and efficient solution for your manufacturing needs.