Table of Contents
The advent of 3D printing has revolutionized various industries, and dentistry is no exception. In dental laboratories, 3D printers have become indispensable tools for producing highly accurate and customized dental appliances. This blog will explore how dental 3D printers work, their scope in dentistry, the types of 3D printing used, the materials involved, the benefits of 3D printing for dentists, and how to choose the right dental 3D printer for your practice.
How Do Dental 3D Printers Work?
Dental 3D printers operate by transforming digital designs into physical models, prosthetics, or surgical guides. The process begins with a digital scan of the patient’s mouth, typically obtained using an intraoral scanner. This scan produces a detailed 3D model of the teeth and surrounding structures, which is then used to design the desired dental appliance or model.
Once the design is finalized using specialized software, the data is sent to the 3D printer. The printer constructs the object layer by layer, using materials such as light-cured resin. The process involves curing each layer of material with a light source, typically a laser or LED, which solidifies the resin. This additive manufacturing process ensures that each layer is precisely placed, resulting in a highly accurate and detailed final product.
The technology allows for the creation of complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This capability is particularly valuable in dentistry, where precision and customization are paramount.
What is the Scope of 3D Printing in Dentistry?
The scope of 3D printing in dentistry is vast, with applications ranging from simple models to complex surgical guides. Here are some of the key areas where 3D printing is making a significant impact:
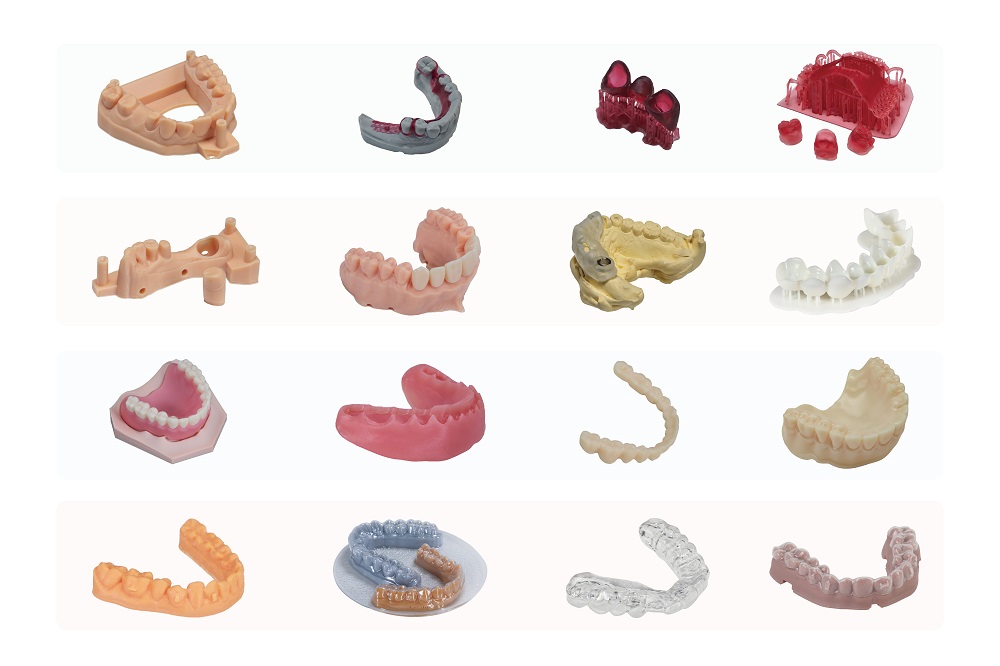

Implants
3D printing plays a crucial role in the fabrication of dental implants. By creating precise models of a patient’s jawbone, dentists can design implants that fit perfectly. This precision reduces the risk of complications and ensures better integration with the patient’s anatomy.
Crowns and Bridges
Crowns and bridges are among the most common dental restorations. 3D printing allows for the rapid production of these restorations with exceptional accuracy, ensuring a perfect fit and natural appearance. The speed of 3D printing also reduces the turnaround time for patients, allowing for quicker restorations.
Surgical Guides
Surgical guides are essential for ensuring the accurate placement of dental implants. 3D printing enables the production of custom guides that match the patient’s anatomy precisely. These guides improve the accuracy of surgical procedures, leading to better outcomes and faster recovery times for patients.
Anatomical Replicas and Models
Dental 3D printing is widely used to create anatomical replicas and models for diagnostic purposes, treatment planning, and patient education. These models help dentists and patients visualize the treatment process, leading to better communication and understanding.
Aligners and Retainers
Clear aligners and retainers are becoming increasingly popular for orthodontic treatment. 3D printing allows for the production of custom aligners that are tailored to each patient’s unique dental structure. This customization ensures more effective treatment and a more comfortable fit.
Casting Models
In restorative dentistry, casting models are used to create molds for dental appliances such as crowns, bridges, and dentures. 3D printing produces highly accurate casting models, ensuring that the final appliances fit perfectly and function properly.
Dentures
3D printing is also used in the production of dentures. The technology allows for the creation of custom denture bases and teeth that match the patient’s anatomy. This results in more comfortable and aesthetically pleasing dentures.
What Type of 3D Printing is Used in Dental Laboratories?
Several types of 3D printing technologies are used in dental laboratories, each with its advantages and applications:
Traditional (Laser-Based) Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA is one of the oldest and most widely used 3D printing technologies in dental laboratories. It uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid plastic, layer by layer. SLA is known for its high resolution and accuracy, making it ideal for producing detailed dental models and appliances.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
DLP is similar to SLA but uses a digital projector screen to flash a single image of each layer across the entire platform, curing the resin all at once. DLP is faster than SLA and can produce highly detailed parts. This speed makes DLP a popular choice for high-volume production in dental laboratories.
Masked Stereolithography (mSLA)
mSLA is a variation of SLA that uses an LCD screen to mask the light source, curing resin in a similar manner to DLP. mSLA offers a balance between speed and resolution, making it suitable for producing dental appliances with fine details and smooth surfaces. It is particularly favored for its efficiency and cost-effectiveness in dental applications.
What Material is Used in Dental 3D Printing?
The most commonly used material in dental 3D printing is light-cured resin. This resin is specially formulated to meet the needs of dental applications, offering properties such as biocompatibility, high strength, and durability. The resin is cured using light sources like lasers or LEDs, resulting in a solid and stable material that can be used for various dental devices.
Light-cured resins come in different formulations, each designed for specific dental applications. For example, some resins are optimized for creating surgical guides, while others are formulated for producing dentures or crowns. The versatility of light-cured resin makes it an ideal material for a wide range of dental 3D printing applications.
What Are the Benefits of 3D Printing for Dentists?
The adoption of 3D printing in dental laboratories offers numerous benefits for dentists, including:
Improved Patient Care and Outcomes
3D printing allows for the creation of highly accurate and customized dental appliances, leading to better fitting devices and improved patient outcomes. The precision of 3D printing ensures that dental restorations are more comfortable and functional, enhancing overall patient satisfaction.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
3D printing streamlines the production process in dental laboratories, reducing the time required to produce dental appliances. This efficiency allows dental practices to serve more patients in less time, improving productivity and profitability.
Better Training for Dentists and Dental Hygienists
3D printed anatomical models provide valuable training tools for dental professionals. These models allow dentists and dental hygienists to practice procedures and improve their skills in a controlled environment, leading to better clinical performance.
Improved Collaboration with Dentists and Suppliers
3D printing enables better collaboration between dental laboratories, dentists, and suppliers. Digital designs can be easily shared and modified, ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned on the final product. This collaboration leads to more efficient workflows and higher-quality outcomes.
How to Choose Dental 3D Printers
Selecting the right dental 3D printer is crucial for ensuring the success of your dental laboratory. Here are some key factors to consider:
Speed and Throughput
The speed of the 3D printer is an important consideration, especially if your laboratory handles a high volume of cases. Faster printers can produce more appliances in less time, improving efficiency and allowing you to meet tight deadlines.
Accuracy and Precision
The accuracy and precision of the printer are critical for producing dental appliances that fit perfectly. Look for printers that offer high resolution and minimal deviation from the digital design.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
A user-friendly 3D printer with straightforward maintenance requirements will save you time and reduce the likelihood of errors. Consider printers with intuitive interfaces and automated features that simplify the printing process.
Cost and Return on Investment
The cost of the printer and the associated materials should be weighed against the potential return on investment. While higher-end printers may have a steeper upfront cost, they often offer better performance and durability, leading to long-term savings.
Materials and Applications
Ensure that the 3D printer you choose is compatible with the materials you plan to use. Some printers are designed for specific types of resin or applications, so it’s important to select a printer that aligns with your needs.
Conclusion
3D printing technology is revolutionizing dental laboratories by offering precise, efficient, and customizable solutions for producing dental appliances. From implants and crowns to surgical guides and dentures, 3D printing plays a crucial role in modern dentistry. By understanding the working principles, types of 3D printing technologies, materials used, and the benefits they offer, dental professionals can make informed decisions when choosing the right 3D printer for their laboratory. The future of dentistry is digital, and 3D printing is at the forefront of this transformation.